what do you mean by keto enol tautomerism Enol tautomerism
Keto Enol Tautomers? Acid and base catalyzed reactions? If these terms sound like gibberish to you, don’t worry, I’m here to enlighten you! Today, we’ll be delving into the fascinating world of keto enol tautomerization and exploring its reaction mechanism in both acidic and basic conditions.
Keto Enol Tautomerization in Acid
 In acidic conditions, keto enol tautomerization involves a series of proton transfers and rearrangements. Let’s break it down step by step. Initially, we start with a reactant known as a keto form (which contains a carbonyl group) and a catalyst (usually an acid like sulfuric acid). The acid donates a proton to the reactant, resulting in the formation of a positively charged intermediate known as an oxonium ion.
In acidic conditions, keto enol tautomerization involves a series of proton transfers and rearrangements. Let’s break it down step by step. Initially, we start with a reactant known as a keto form (which contains a carbonyl group) and a catalyst (usually an acid like sulfuric acid). The acid donates a proton to the reactant, resulting in the formation of a positively charged intermediate known as an oxonium ion.
Next, the oxonium ion undergoes a rearrangement, shifting the proton position to a different carbon atom within the molecule. This rearrangement happens due to the instability of the positive charge and the preference for the formation of a more stable enol form. The enol form contains a double bond and a hydroxyl group (hence the name “enol” derived from alkene + alcohol).
Finally, the enol form can undergo another proton transfer, this time from the catalyst, leading to the formation of the final product, the keto form. This process is reversible, and the equilibrium between the keto and enol forms depends on the specific reaction conditions.
Keto Enol Tautomerization in Base
 Now, let’s switch gears and explore keto enol tautomerization in basic conditions. In the presence of a base (such as sodium hydroxide), the reaction mechanism takes a slightly different path. Similar to the acid-catalyzed reaction, the base donates a hydroxide ion instead of a proton to the keto form.
Now, let’s switch gears and explore keto enol tautomerization in basic conditions. In the presence of a base (such as sodium hydroxide), the reaction mechanism takes a slightly different path. Similar to the acid-catalyzed reaction, the base donates a hydroxide ion instead of a proton to the keto form.
The hydroxide ion attacks the keto reactant at the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl group, resulting in the formation of an oxyanion intermediate. This intermediate is negatively charged due to the addition of the hydroxide ion. From here, a rearrangement takes place to stabilize the negative charge by tautomerizing into the enol form.
As in the acid-catalyzed reaction, the enol form is not the final product. To complete the tautomerization process, another proton transfer occurs, this time from a water molecule. This proton transfer leads to the formation of a hydroxide ion and the desired keto form.
Overall, keto enol tautomerization plays a critical role in various chemical reactions. It involves the interconversion between keto and enol forms through the transfer of protons or hydroxide ions. Understanding the reaction mechanism in both acidic and basic conditions allows chemists to manipulate these tautomeric forms for different applications.
So, the next time you come across the term “keto enol tautomerization,” remember the fascinating interplay between acids, bases, and the rearrangement of chemical structures. This process serves as a fundamental concept in organic chemistry and provides a gateway to numerous possibilities in synthesizing novel compounds and understanding their reactivity. Stay curious and keep exploring the incredible world of science!
If you are searching about Keto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, and Mechanism you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Pics about Keto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, and Mechanism like Keto Enol Tautomerism - What Is It and Why Is It Important?, See question number 2, and please explain how do you determine whether and also See question number 2, and please explain how do you determine whether. Here it is:
Keto-Enol Tautomerism: Definition, Examples, And Mechanism
 www.chemistrylearner.comenol tautomerism
www.chemistrylearner.comenol tautomerism
Keto Enol Tautomerism - What Is It And Why Is It Important?
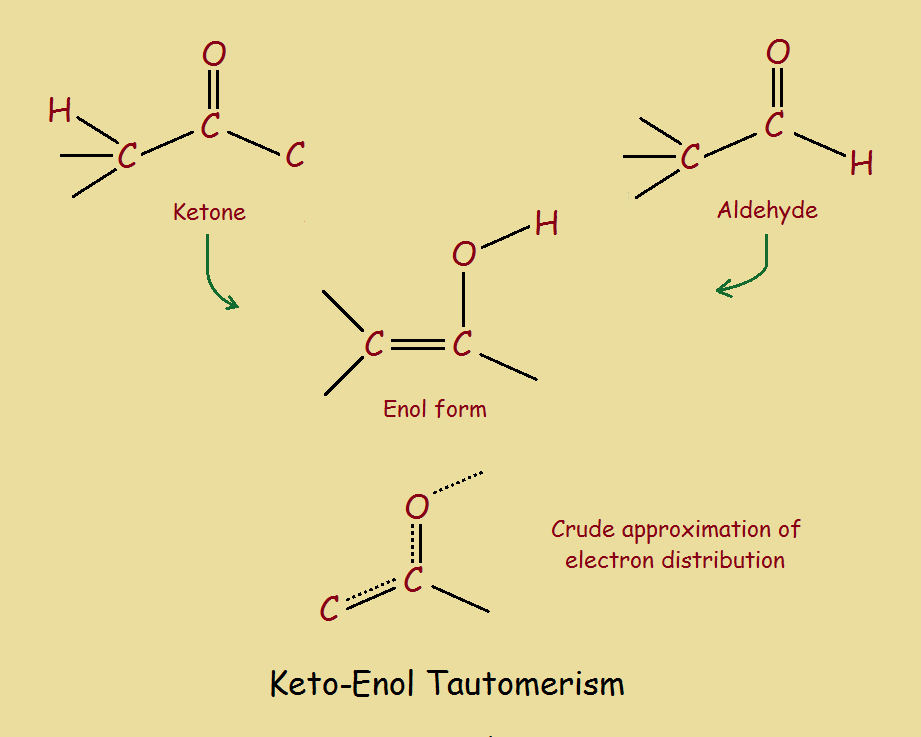 www.quirkyscience.comenol keto tautomerism chemistry xef4 quirkyscience ensuing attention
www.quirkyscience.comenol keto tautomerism chemistry xef4 quirkyscience ensuing attention
See Question Number 2, And Please Explain How Do You Determine Whether
 www.meritnation.comKeto Enol Tautomerization Reaction And Mechanism In Acid And Base
www.meritnation.comKeto Enol Tautomerization Reaction And Mechanism In Acid And Base
 leah4sci.comenol tautomerization ketone catalyzed ket tautomers leah4sci molecules
leah4sci.comenol tautomerization ketone catalyzed ket tautomers leah4sci molecules
Concept For PHIP Of Keto-enol Tautomerized Substances. (a) Keto-enol
 www.researchgate.netenol keto tautomerism tautomer phip substances ketone equilibrium
www.researchgate.netenol keto tautomerism tautomer phip substances ketone equilibrium
See question number 2, and please explain how do you determine whether. Keto enol tautomerization reaction and mechanism in acid and base. Concept for phip of keto-enol tautomerized substances. (a) keto-enol